Model tiering is typically determined in four moments during the life of a model:
- At inception, when the model is added to the inventory before it goes to model validation and then production. This may be important to decide the level of details of the model validation itself;
- As part of (periodic) model validation, where both model owners and validators review the latest model tier;
- As part of a regular (e.g. annual) model attestation, where the model risk management team requests model owners to certify model tiers, e.g. a change in exposure leads to a new materiality level that may in turn trigger a tier change;
- An ad-hoc model tier update, due to a significant change in the model that cannot wait until one of the above events takes place (see Extract 1).
Extract 1: Ad hoc model tiering workflow in Yields for Governance.
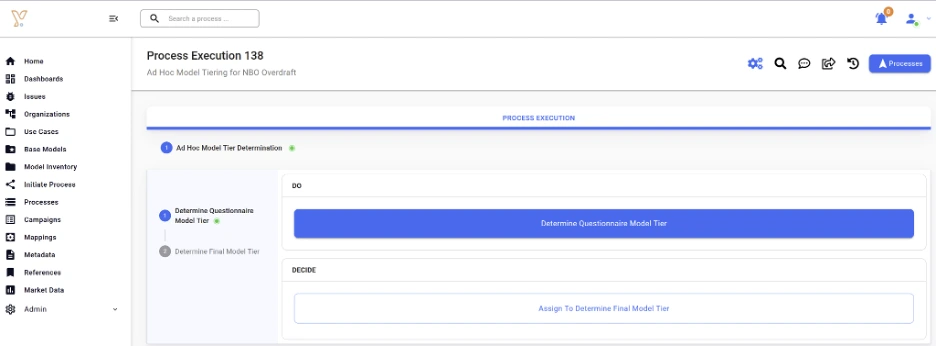
We now look at the regulatory guidelines on model tiering one by one, with our complementary observations when required, and briefly describe how the Yields MRM suite addresses the requirements.
1. Firm-wide consistent tiering approach for all models – to ensure all models have an associated risk level and prioritization is made possible.
Yields MRM Platform Solution:
Model owners perform a self-assessment for each risk driver, determining the tier via the use of questionnaires (first action in the workflow of Extract 1). In Chiron Enterprise, questionnaires:
- are configurable from the UI,
- allow the flexibility to be specified as:
- one for all models, to ensure full consistency across the inventory, or
- one per model type, to be able to capture elements that are idiosyncratic to a given family of models, e.g. a questionnaire for ML models may include an explicit assessment of explainability in the complexity dimension.
- can embed logic to automatically determine the tier based on the level of the risk drivers. This can be as simple as defining a tier value for each combination (materiality, complexity) or even based on a computed weighted average score.
Extract 2: Example of a basic questionnaire
HIGH complexity and HIGH materiality automatically lead to “Tier 1”.
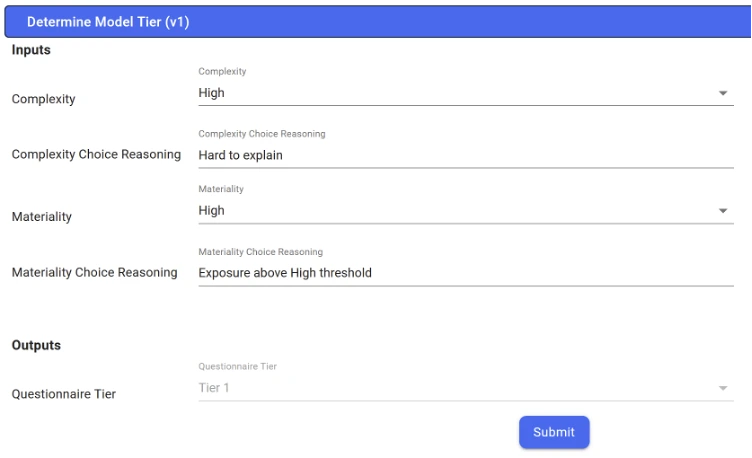
2. Model materiality and complexity assessments
Model materiality should include both quantitative and qualitative measures.
Quantitative measures may include:
- exposure,
- book/market value,
- the number of affected users the model relates to.
Qualitative measures reflect model reliance, e.g. usage of the model for (non-)critical business decisions.
Model complexity may take into account:
- the inherent risk of the model, e.g. assumptions, limitations and interdependencies,
- explainability and bias.
Yields MRM Solution:
When it comes to assessing quantitative aspects of model materiality, an example is to run simple scripts in Chiron App to aggregate model exposure and compare it against defined thresholds to determine the level of materiality (e.g. HIGH if aggregate model exposure is higher than £10M). As for qualitative measures, the user may be asked to provide supporting evidence, e.g. by attaching a file.
Extract 3: Providing supporting evidence in tier determination
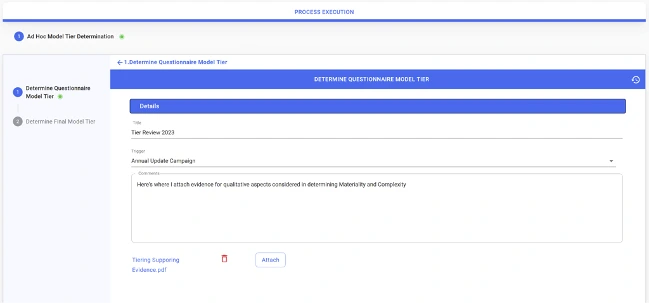
For explainability and bias, a mix of quantitative and qualitative analysis can be conducted. For the former, scripts can be run in the Chiron App platform to run tests such as ‘Shapley Values’ and ‘Feature Importance’ for explainability, and ‘Statistical Parity’ and ‘Equal Opportunity Difference’ for bias analysis. Supporting evidence of qualitative elements can also be attached, as in the case of materiality.
For model complexity, as inherent risk factors can be captured directly in the model inventory, model owners can easily access this information as part of their self-assessment.
Extract 4: Capturing model limitations in the Chiron Enterprise platform.
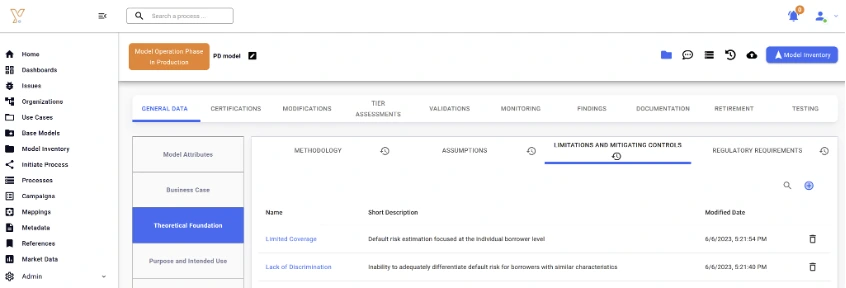
For explainability and bias, a mix of quantitative and qualitative analysis can be conducted. For the former, scripts can be run in the Chiron App platform to run tests such as ‘Shapley Values’ and ‘Feature Importance’ for explainability, and ‘Statistical Parity’ and ‘Equal Opportunity Difference’ for bias analysis. Supporting evidence of qualitative elements can also be attached, as in the case of materiality.
3. Periodic review of the tiering approach – to ensure that the approach continues to be valid for a given organization’s reality and that the model inventory information in relation to the model’s tier is kept up to date.
Yields MRM Solution:
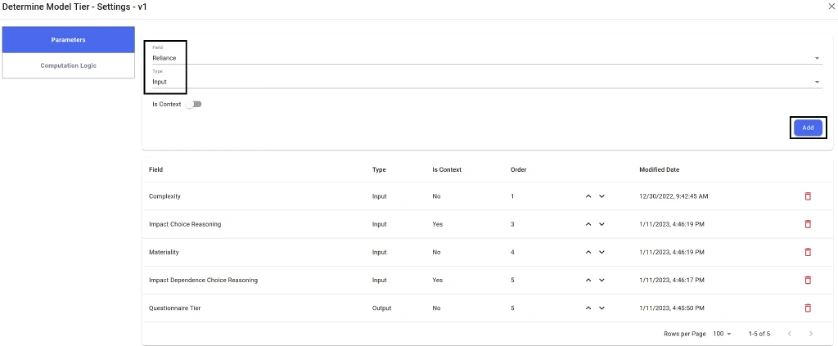
Given its full configurability from the UI, questionnaires and model tiering workflows can be modified at any time to reflect any (structural) changes in the process. For example, if the number of models in the inventory is increased substantially, an additional independent risk driver such as Model Reliance may need to be added to achieve higher granularity.
Extract 5: Updating a tiering questionnaire structure in Chiron Enterprise
In order to ensure the model tier is up to date across all models in the inventory, the Campaigns functionality can be leveraged in Chiron Enterprise. This facilitates a centralized execution of model tiering across multiple models in parallel (e.g. as part of the model attestation initiative mentioned above).
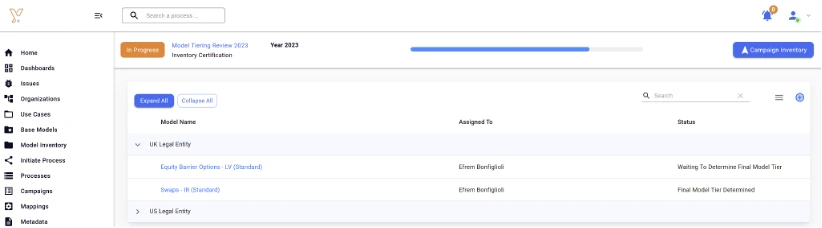
A campaign is a collection of workflows (e.g. Model Tiering) that can be run and monitored centrally in parallel for a timely end-to-end execution. As one can imagine, validation and monitoring activities could also leverage a campaign’s functionality.
In Extract 6 below we can see how the model tiering process status is followed for all models (e.g. 2 in the UK legal entity) in the scope of the campaign.
Extract 6: Example of a model tiering campaign in Chiron Enterprise
4. Independent re-assessment of the model tiering determination components as part of the (periodic) validation activities.
Yields MRM Solution:
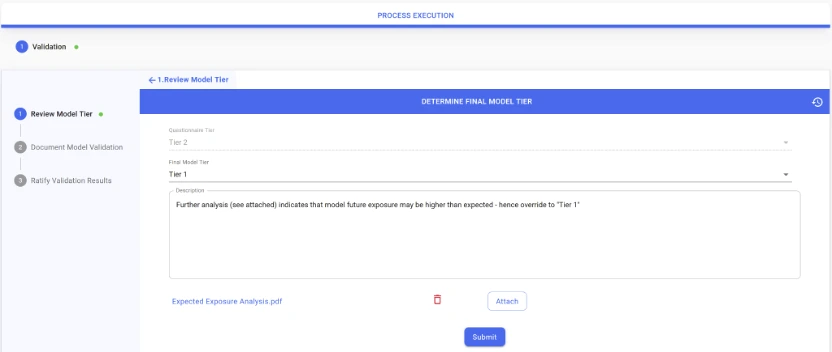
In Chiron Enterprise, as part of model validation, validators can review the latest model tier self-assessment and can be empowered to decide on the correct final model tier, potentially after overrides, as in the example below.
Extract 7: The model tier is reviewed and finalized by model validation
Model validators can also independently re-run scripts in Chiron App to check the quantitative measures involved in tier determination (as discussed in Section 2 above).




